# vuex
概念
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化
# 状态管理模式
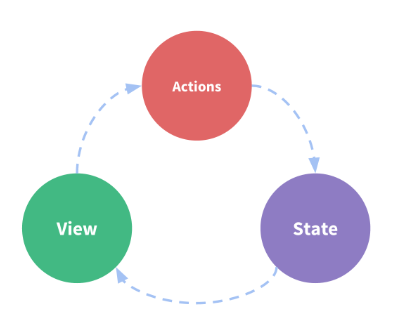
状态管理包括下面几个部分:
state驱动应用的数据源view声明式将state映射到视图actions响应视图上用户操作导致的状态变化
# 使用场景
在多个组件共享状态时,单向数据流的简洁性很容易被破坏:
- 多个视图依赖于同一状态:传参对于多层嵌套组件会非常繁琐,并且对于兄弟组件间的状态传递无能为力
- 来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态:父子组件直接引用或者通过事件和同步状态的多份拷贝
上面的情况会导致代码难以维护,所以需要报共享状态抽取,用全局单例模式管理。
# 核心概念
# State
vuex 使用单一状态树,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态,也意味着,每个应用将仅仅包含一个 store 实例。单一状态树让我们能够直接地定位任一特定的状态片段,在调试的过程中也能轻易地取得整个当前应用状态的快照。
vue 中展示状态:
- 计算属性 单个状态
mapState多个状态
# Getter
需要通过 state 中派生出一些状态的时候,可以通过 Getter 来实现
vue 中展示状态:
- 计算属性
store.getters.doneTodos单个状态 mapGetters多个状态
# Mutation
修改 store 中状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation:this.$store.commit('xxx')
mutation 必须是同步函数,如果是异步的状态的改变无法追踪
# Action
类似 Mutation:
Action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态。Action可以包含任意异步操作。
分发 Action:
// 以载荷形式分发
store.dispatch("incrementAsync", {
amount: 10
});
// 以对象形式分发
store.dispatch({
type: "incrementAsync",
amount: 10
});
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
异步和分发多重:
actions: {
checkout ({ commit, state }, products) {
// 把当前购物车的物品备份起来
const savedCartItems = [...state.cart.added]
// 发出结账请求,然后乐观地清空购物车
commit(types.CHECKOUT_REQUEST)
// 购物 API 接受一个成功回调和一个失败回调
shop.buyProducts(
products,
// 成功操作
() => commit(types.CHECKOUT_SUCCESS),
// 失败操作
() => commit(types.CHECKOUT_FAILURE, savedCartItems)
)
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
组件中分发:
import { mapActions } from "vuex";
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
"increment", // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
"incrementBy" // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: "increment" // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
组合 action:
// 假设 getData() 和 getOtherData() 返回的是 Promise
actions: {
async actionA ({ commit }) {
commit('gotData', await getData())
},
async actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
await dispatch('actionA') // 等待 actionA 完成
commit('gotOtherData', await getOtherData())
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Module
当应用规模比较大的时候,可以通过模块 module 来划分,每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter,甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割:
const moduleA = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 严格模式
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...
strict: true
});
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
在严格模式下,无论何时发生了状态变更且不是由 mutation 函数引起的,将会抛出错误。这能保证所有的状态变更都能被调试工具跟踪到。